Rapid Application Development with Groovy
November 01, 2007
While i was cleaning up my hard disk on my Linux in 2007, i needed a program that displays the disk usage graphically. I didn't find a suitable one on the web. At that time i was learning Groovy and it's for rapid application development, isn't it. So i gave it a try.
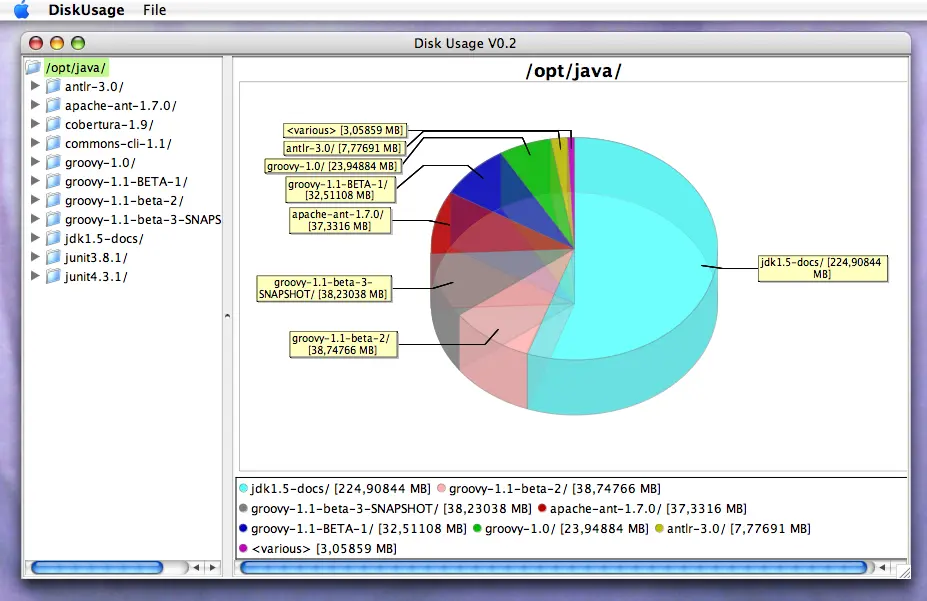
Requirements: The user chooses a directory, then the directory structure is displayed as a tree and a pie chart is displayed that shows the usage of disk space. If the user selects a subdirectory it's disk space usage will be shown in the pie chart.
The chart is drawn using the JFreeChart library which is written in Java. This is one of the reasons i switched from Perl to Groovy: the high quality libraries available.
Notes on Design and Implementation
Overview
Basically there are the three programming tasks.
- The contents of the directory, i.e. its subdirectories and files, have to be analyzed and stored.
- The graphical user interface has to be designed and implemented.
- The chart has to be drawn and fed with the data from step 1.
Step 1
For step 1 there is a straightforward recursive algorithm that
is easy to implement if one knows the Java File class.
The data will be stored in a tree data structure.
Step 2
The implementation of the GUI with the Groovy Swing Builder is rather a specification with a domain specific language (DSL). The window in the screenshot above is implemented with simple statements like the following.
def swing = new SwingBuilder()
def frame = swing.frame(title: 'Disk Usage V0.2', layout: new GridLayout(1,1),
minimumSize: [width: 600, height: 500], defaultCloseOperation:WC.EXIT_ON_CLOSE) {
menuBar {
menu(mnemonic: 'F', 'File') {
menuItem(action: actionChoose)
separator()
menuItem(action: actionExit)
}
menu(mnemonic: 'H', 'Help') {
menuItem(action: actionAbout)
}
}
splitPane(id: 'panes') {
scrollPane(minimumSize: [width: 200, height: 100]) {
tree = tree(id: 'tree', model: treeModel, cellRenderer: renderer)
}
scrollPane() {
panel(id:'canvas', layout: new GridLayout(1,1) ) {
widget(new ChartPanel(chart))
}
}
}
}
The hierarchical structure of a Swing GUI is reflected by the opening and closing braces.
For all the Swing-Jxyz classes there is a "wrapper" function used in the SwingBuilder,
e.g. "menu" for "JMenu". The actions and the dialogs are defined as following.
def actionAbout = swing.action( name:'About ...', closure: this.&actionAbout, mnemonic: 'A', accelerator: 'F1' )
def fileChooserDialog = swing.fileChooser(id: 'fileChooser', fileSelectionMode: JFileChooser.DIRECTORIES_ONLY )
DefaultTreeCellRenderer renderer = new DefaultTreeCellRenderer()
renderer.setLeafIcon(renderer.getClosedIcon()) // Only display folder icons in the treeSee the source code for all the details. The pie chart is initialized and configured with the following statements.
def piedataset = new DefaultPieDataset(); // the data of the chart
def chart = ChartFactory.createPieChart3D('untitled', piedataset, true, true, true)
chart.backgroundPaint = Color.white
PiePlot3D pieplot3d = (PiePlot3D) chart.getPlot();
pieplot3d.setForegroundAlpha(0.6F);
pieplot3d.setNoDataMessage('No data to display');Step 3
The dataset of the pie chart is updated with the following piece of code. The class Element
is a node in the directory tree.
private void updatePieDataSet(Element node) {
piedataset.clear()
for (child in node.children) {
piedataset.setValue(child.format(format), child.sum)
}
}Conclusion
With Groovy rapid application development is possible, provided you have enough practise with Java libraries and Groovy's features.
Extension 2012: Parallelization with GPars
I improved the performance with GPars.
A new thread pool is startet with GParsPool.withPool and for each directory a new task is created
with GParsPool.runForkJoin.
Download
The code is available at GitHub.